Did you know that emerald ash borers can kill a healthy ash tree in as little as one to three years? This relentless pest is responsible for the deaths of millions of ash trees across the United States, causing a cascade of ecological and financial distress for communities, homeowners, and cities. Immediate action with the right ash borer insecticide treatments is the only way to halt the devastation and save your ash trees before it’s too late. In this guide, you'll learn everything you need to know to fight back, including proven products, application strategies, and when to seek professional help.
A Startling Fact: The Urgent Threat of Emerald Ash Borer and Fast-Acting Ash Borer Insecticide Treatments
The emerald ash borer (EAB) is a highly destructive invasive insect that specifically targets ash trees. Since its discovery in North America, EAB has spread across 35 states, decimating once-thriving urban and rural forests. Infested ash trees can lose their entire canopy in two to three years, progressing from outwardly healthy to dead with alarming speed. Without quick intervention, property owners may face high costs for tree care, removal, and even a decrease in property values. Because ash borer insecticide treatments act as the primary line of defense, acting swiftly when symptoms are first observed is vital.
The high mortality rate caused by emerald ash borers comes with a steep economic toll: cities and homeowners have spent billions on the removal of infested trees and preventive treatments. Fast-acting insecticide treatments can rapidly stop further damage, allowing ash trees to recover and thrive. Prioritizing prompt application not only saves individual trees but also prevents a domino effect of infestation throughout neighborhoods. When facing this threat, choosing a proven, quick-response insecticide treatment makes all the difference in successfully preserving your ash trees .
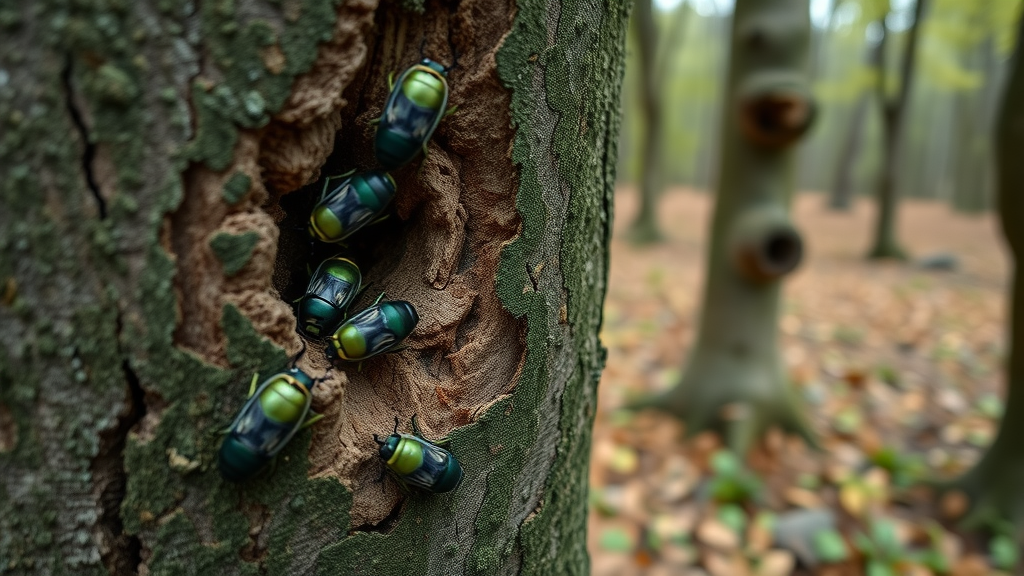

What You Need to Know: Why Swift Ash Borer Insecticide Treatments Matter for Ash Trees
Overview of emerald ash borer infestation rates: Emerald ash borers spread rapidly, with localized infestations capable of killing ash trees within three years of detection. EAB populations can double annually in ideal conditions.
Economic impact of ash borer damage: Cities, counties, and homeowners face increased costs for emergency tree removal and treatment—sometimes totaling thousands of dollars per yard or property.
Importance of immediate insecticide treatment for ash trees: Targeted insecticide applications can suppress active infestations, reducing canopy thinning and enabling infested trees to recover more quickly.
Understanding Emerald Ash Borer: How Ash Borer Infestations Harm Ash Trees
The emerald ash borer attacks all species of North American ash trees, boring beneath the bark and disrupting the tree’s ability to transport water and nutrients. This damage accelerates canopy thinning , bark splits, and overall decline. Once the pest establishes itself, it can be challenging to control, which is why early identification and prompt ash borer insecticide treatments are essential.
Infested ash trees often exhibit rapid symptom progression, making immediate response crucial. Unchecked, these pests leave neighborhoods filled with dead and dying ash trees , attracting other pathogens and pests while imposing significant costs and community losses. By understanding the pest's biology and identifying infestation early, property owners can beat the clock with effective, fast-acting solutions.
The Life Cycle and Behavior of the Emerald Ash Borer
The emerald ash borer has a one-to-two-year life cycle, depending on local climate conditions. Adults emerge from infested ash trees in late spring and early summer, seeking out new hosts for egg-laying. Eggs hatch into larvae, which tunnel beneath the bark, feeding on the vital cambium layer. This “hidden” feeding is what kills the tree, as it disrupts nutrient and water flow.
As the larvae mature, they create distinctive S-shaped tunnels that weaken the ash tree’s structure. Pupation and emergence of adult beetles typically occur the following spring. This annual cycle means infestations can go unnoticed until severe damage has occurred, emphasizing the necessity for vigilant monitoring and timely application of insecticide treatments to target the most vulnerable stages.
Recognizing an Infested Ash Tree: Critical Signs to Watch For
Symptoms of infested ash: bark splits, canopy thinning: Signs include vertical splits in the bark, the presence of D-shaped exit holes from emerging beetles, and a rapidly thinning canopy. Sometimes, you’ll see epicormic shoots sprouting from the tree’s base as it struggles to survive.
Visual cues on ash trees from emerald ash borer activity: Look for frass (sawdust-like waste) around the base, woodpecker activity (birds feeding on larvae), or distinct serpentine tunnels beneath the bark—all indicators that ash borer insecticide treatments are urgently needed.
How Ash Borer Insecticide Treatments Work: Safeguarding Emerald Ash Trees
Advances in chemical control have made it possible to target emerald ash borer quickly and effectively using dedicated ash borer insecticide treatments . These products interrupt EAB’s lifecycle either by killing larvae as they feed inside the tree or trapping adults as they emerge. When applied correctly, certain treatments can reverse early decline and significantly increase an ash tree’s survival odds.
The two primary approaches involve systemic insecticides , which are absorbed by the tree to kill internal larvae, and contact insecticides that target adult beetles on the surface. Each strategy has its own ideal application method, timing, and suitability for specific levels of infestation, making it important for property owners to choose the right product for their needs.
Modes of Action in Ash Borer Insecticide Treatments
Systemic vs. contact insecticide treatment: Systemic insecticides are applied as soil drenches, trunk injections, or bark sprays, allowing the tree to distribute the active ingredients (such as imidacloprid, emamectin benzoate, or dinotefuran) throughout its vascular system. Contact insecticides generally coat the tree bark, killing adult beetles on contact but offering less protection against larvae.
Common chemical agents for ash borer control (imidacloprid, emamectin benzoate): Imidacloprid is well suited for early intervention and soil treatments, while emamectin benzoate is a potent trunk-injectable agent, frequently used for moderate to severe infestations. Dinotefuran serves as a bark spray, providing the fastest knockdown of active EAB adults and larvae.
Choosing between these insecticide options depends on the size of your tree, the level of infestation, and how quickly you need results. Following all label instructions and consulting a certified arborist can greatly improve success rates while reducing risks to non-target wildlife and plants.
Why Speed Matters: Immediate Response to Emerald Ash Borer for Ash Trees
"Rapid intervention with targeted insecticide treatments prevents irreversible damage to ash trees from emerald ash borer, saving communities thousands of dollars in tree removal costs." – Arborist Expert
Once symptoms of emerald ash borer infestation appear, the window to save an infested ash tree can be narrow—sometimes less than a single growing season. Fast-acting ash borer insecticide treatments rapidly halt further damage and starve the larvae, giving the tree the chance to heal and regrow foliage in the following year. Waiting too long often results in significant decline or death, requiring costly tree removal and increasing the risk of spreading EAB to other nearby trees.
Acting swiftly is especially important for valuable landscape ash trees, large trees, or those in neighborhoods with high EAB activity. Coordinated action with proven products helps prevent the loss of community tree canopy and reduces the long-term impact of this invasive pest.
Comprehensive List of Ash Borer Insecticide Treatments for Immediate Results
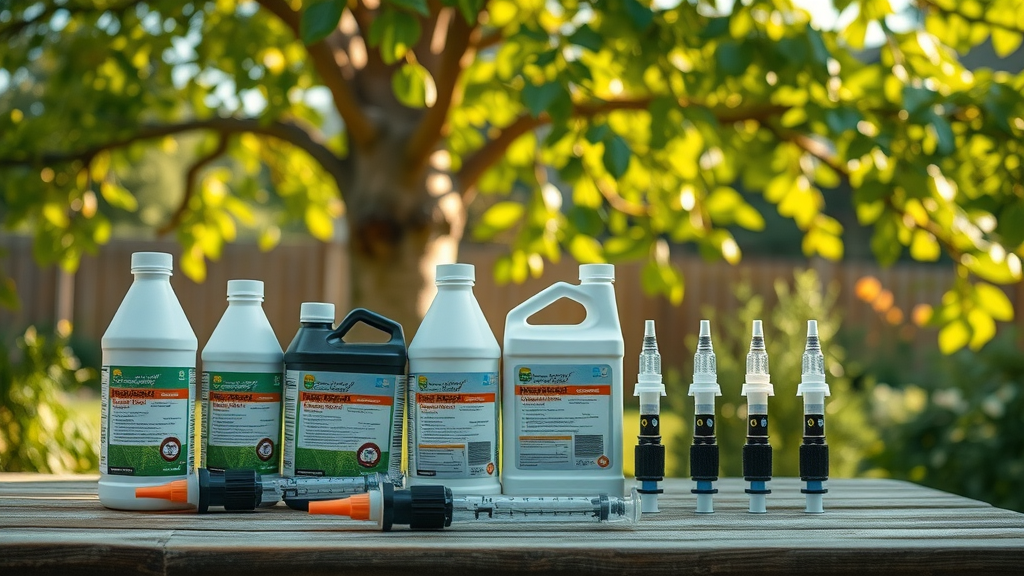

Recommended insecticide treatments for emerald ash borer: Top choices include emamectin benzoate trunk injections for rapid reversal, imidacloprid soil drench for early protection, and dinotefuran bark sprays for the fastest observable knockdown of EAB activity.
Pros and cons of each insecticide option for ash trees: Trunk injections deliver concentrated treatment fast but require equipment and expertise; soil drenches offer broader coverage for DIY, though results take longer; bark sprays work quickly on adults but may require repeat applications.
Top-rated products: how quickly results appear: Emamectin benzoate injections can save severely infested trees within 7-14 days; imidacloprid drenches show protection after 3-4 weeks; dinotefuran bark spray reduces EAB activity in 1-2 weeks.
Product |
Active Ingredient |
Application Method |
Speed of Effect |
Ideal For |
|---|---|---|---|---|
Emamectin Benzoate |
Emamectin Benzoate |
Trunk Injection |
7-14 Days |
Severely infested ash trees |
Imidacloprid |
Imidacloprid |
Soil Drench |
3-4 Weeks |
Early stage infestation |
Dinotefuran |
Dinotefuran |
Bark Spray |
1-2 Weeks |
Immediate reduction in emerald ash borer activity |
DIY vs. Professional Ash Borer Insecticide Treatments
When to attempt do-it-yourself solutions: Soil drench and bark spray ash borer insecticide treatments are suitable for small to medium ash trees, especially in early infestation. Homeowners should always follow safety and label instructions.
Benefits and risks compared with licensed applicators: While DIY treatment is more accessible and affordable, professional pesticide applicators have experience and equipment for accurate diagnosis, proper dosing, and application—crucial for large or precious ash trees and severe infestations. Professionals can select and apply trunk injection products (like emamectin benzoate), which are the gold standard for advanced EAB control and recovery.
In most cases, hiring a certified arborist or licensed professional is the best approach for treating highly valuable, large, or severely infested ash trees . Their expertise ensures both effectiveness and environmental safety, especially when powerful active ingredients are involved.
Selecting the Best Insecticide Treatment for Your Infested Ash Tree
Choosing the right insecticide treatment depends on careful assessment of your tree’s size, health, and the extent of emerald ash borer infestation. Matching the right product and method to these factors is essential for quick and successful outcomes.
For landscape trees that provide significant shade, curb appeal, or historic value, consulting with a certified arborist is recommended. An expert can tailor insecticide treatments for your scenario, considering regional EAB activity, product restrictions, and environmental factors to safeguard your ash trees most effectively.
Factors to Consider: Tree Size, Infestation Level, and Emerald Ash Borer Risk

Evaluating ash tree health before treatment: Trees with more than 30% canopy thinning or heavy bark splits may have limited recovery potential. However, trees with minimal dieback are excellent candidates for systemic ash borer insecticide treatments .
Matching insecticide options to infestation severity: For small, early-stage infestations, soil drenches work well. For significant or rapidly progressing damage, trunk injections and bark sprays offer prompt relief and survival prospects.
Take into account the age, species, and site conditions of your ash tree before selecting an insecticide treatment . This assessment ensures you invest in the most promising recovery and protection methods.
Timing Matters: Optimal Application Times for Ash Borer Insecticide Treatments
"For maximum efficacy, apply imidacloprid in early spring before the emergence of adult emerald ash borers." – University Extension Specialist
Timing is critical to successful ash borer insecticide treatments . Applying imidacloprid or dinotefuran soil drenches is most effective in early spring, as this gives the tree time to absorb the product and protect itself before adult beetles emerge. Trunk injections with emamectin benzoate also provide continued protection when applied during or just before peak EAB activity.
Late spring and early summer are also suitable for some products, especially in regions where adult beetle emergence may be delayed. Always refer to local county extension office recommendations, product dosing, and application instructions for the best chance at saving your ash trees from emerald ash borer.
Step-by-Step Guide: How to Apply Ash Borer Insecticide Treatments Safely and Effectively
Assess if your ash tree is at risk from emerald ash borer: Identify visible signs and check for local EAB activity via the department of agriculture or minnesota department of agriculture updates.
Select the appropriate insecticide treatment: Choose a soil drench, trunk injection, or bark spray based on tree size and infestation level.
Prepare and apply the chosen insecticide: Gather all necessary equipment, follow label instructions, and wear proper protective gear before application.
Monitor results and repeat treatment as needed: Observe for signs of recovery or persistent decline, and follow up with additional treatments if instructed.

Safety Precautions for Homeowners Using Insecticide Treatments
Personal protective equipment required for emerald ash borer treatments: Always wear gloves, goggles, and long sleeves to protect yourself from spills and chemical exposure. Wash hands thoroughly after handling any insecticide product .
Environmental considerations and proper disposal: Avoid contaminating water sources by following manufacturer guidance and never dispose of leftover solutions in drains or water bodies. Use only approved products, and store chemicals out of reach of children and pets.
If you’re uncertain, consult with a local pesticide applicator for safe handling and disposal, and always adhere to regional department of agriculture regulations regarding pesticide usage on residential properties.
Maintaining Healthy Ash Trees After Insecticide Treatment
Post-treatment care is essential for helping ash trees bounce back from emerald ash borer infestation. Even after successful insecticide treatments , ongoing maintenance ensures continued health and resistance.
Mulching, watering during drought, and routine inspections complement chemical control. Pruning dead wood, watching for new symptoms, and keeping the area beneath the canopy free from stressors allow the ash tree to devote its energy towards recovery.
Recovery Timeline for Infested Ash Trees Treated with Fast-Acting Insecticide
How quickly ash trees bounce back after insecticide treatment: Trees treated in the early stages of infestation can show signs of renewed growth, increased leaf density, and reduced borer activity within one growing season. Full canopy restoration may take one to two years depending on the level of pre-treatment decline.
Signs of recovery and ongoing care recommendations: Indicators include healthy new shoots, less canopy thinning, and absence of new exit holes or frass. Continue annual treatments, periodic inspections, and cultural practices (watering, mulching) to maintain tree vigor.

Preventing Future Emerald Ash Borer Infestations with Insecticide Treatments
Best practices for annual maintenance: Apply preventive ash borer insecticide treatments each year in high-risk areas, especially for prized or highly visible ash trees .
Neighborhood-wide approaches to emerald ash borer management: Encourage coordinated treatments throughout communities to create an inhospitable environment for EAB and reduce overall pressure on surviving trees.
Consider working with local tree care organizations, city foresters, or regents of the university extension services to monitor EAB risks and plan synchronized protective measures for your entire area.
Answering Common Questions on Ash Borer Insecticide Treatments
Do it yourself emerald ash borer treatment?
Yes, some ash borer insecticide treatments are available for homeowners as DIY solutions. Soil drenches and trunk sprays can be applied following all safety guidelines, but trunk injection is often more effective and is best left to professionals for optimal results. Proper identification and timing are critical in DIY treatments for emerald ash borer.
What time of year should I treat my emerald ash borer?
The ideal time for ash borer insecticide treatments is in early spring, when emerald ash borer larvae are most vulnerable, and before adults emerge. Late spring and early summer are also effective windows, depending on local emerald ash borer activity.
When to apply imidacloprid for emerald ash borer?
Imidacloprid should be applied as an insecticide treatment for ash borer in the early spring to allow the tree to absorb the chemical before active emerald ash borer feeding begins. This maximizes the protective effect for ash trees.
Can a tree recover from ash borer?
Ash trees can recover from emerald ash borer infestations if detected early and treated quickly with effective insecticide treatments . Severely infested ash trees, however, may be beyond recovery. Ongoing monitoring and preventive treatments increase the likelihood of survival.
Summary of Key Takeaways for Ash Borer Insecticide Treatments
Fast action is crucial for emerald ash borer threats
Effective insecticide treatments can save ash trees
Proper timing and method of insecticide treatment greatly improve outcomes
Ready to Protect Your Ash Trees? Take Action with Proven Ash Borer Insecticide Treatments
Act now—don’t wait for visible decline. Use trusted, fast-acting ash borer insecticide treatments today to save your valuable ash trees and keep your landscape healthy for years to come!
 Add Row
Add Row  Add
Add 




Write A Comment